假设要在n个城市之间建立通信网络,则连通n个城市只需要n-1条线路。现在想节省光缆,使得路径和最小。
这一问题就是最小代价生成树问题(Minimum Cost Spanning Tree),简称MST。
MST性质:假设N=(V, {E})是一个连通图,U是顶点集合V的一个非空子集,若(u, v)是一条具有最小权值的边,u属于U且v属于V-U。则必存在一棵包含边(u, v)的最小生成树。
因此,可以采用贪心算法解决。
1、Prim(普里姆)算法
我们需要设置两个辅助数组cost和ivex,它们需要联合在一起使用。
i表示一个尚未被选择的顶点的下标(尚属于V-U)。cost[i]为U中所有顶点中到i的最小权值,ivex[i]即为U中的这个顶点。
因此初始情况下,我们使得ivex[*] = v0, cost[i] = arcs[v0][i]。
每次,选择cost最小的一个的i,然后ivex[i]就是新选择边的起始点,i就是终结点。
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <memory.h>
#define MAX_VNUM 100
#define INF_DIST 0xfffffff
#define COST_SELECT -1
typedef struct
{
int vexs[MAX_VNUM]; // vertex(s)
int nvexs; // number of vertex(s)
int arcs[MAX_VNUM][MAX_VNUM]; // arc(s)
int narcs; // number of arc(s)
} Graph;
int graph_locate_vec(Graph* graph, int val)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<graph->nvexs; i++)
{
if(graph->vexs[i]==val)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void graph_create_graph(Graph* graph)
{
int i, j;
// 存储顶点
printf("Please enter n for vex(s) :n");
scanf("%d", &graph->nvexs);
for(i=0; i<graph->nvexs; i++)
{
printf("Please enter a int for vecs(%d) :n", i);
scanf("%d", &graph->vexs[i]);
}
// 存储弧度
//memset(graph->arcs, INF_DIST, sizeof(int)*MAX_VNUM*MAX_VNUM);
for(i=0;i<graph->nvexs;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<graph->nvexs;j++)
{
graph->arcs[i][j] = INF_DIST;
}
}
printf("Please enter m for arc(s) :n");
scanf("%d", &graph->narcs);
for(i=0; i<graph->narcs; i++)
{
int x, y, w;
printf("Please enter v1, v2, w for vecs(%d) :n", i);
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &w);
x = graph_locate_vec(graph, x);
y = graph_locate_vec(graph, y);
if(x==-1 || y==-1)
{
i--;
printf("Invalid v1 or v2.n");
continue;
} else if (w<=0)
{
i--;
printf("Invalid w.n");
continue;
}
graph->arcs[x][y] = w;
graph->arcs[y][x] = w;
}
}
// Minimum Cost Spanning Tree using Prim
void mst_prim(Graph* g)
{
int k;
int i;
int j;
int ivex[MAX_VNUM];
int cost[MAX_VNUM];
k = 0; // First vec in U
cost[k] = COST_SELECT;
// Init cost with u -> i (i is vex in V-U)
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
if(i!=k)
{
ivex[i] = k;
cost[i] = g->arcs[k][i];
}
}
// Select other nvex-1
for(i=1; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
// Select min cost[i] and i is not select yet
int min=INF_DIST, min_vex=0;
for(j=0; j<g->nvexs; j++)
{
if(cost[j]!=COST_SELECT && cost[j]<min)
{
min_vex = j;
min = cost[j];
}
}
k = min_vex;
cost[k] = COST_SELECT;
printf("Arc %d -> %d n", g->vexs[ivex[k]], g->vexs[k]);
// Update unselect cost
for(j=0; j<g->nvexs; j++)
{
if(cost[j]!=COST_SELECT && g->arcs[k][j]<INF_DIST && g->arcs[k][j]<cost[j])
{
ivex[j] = k;
cost[j] = g->arcs[k][j];
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Graph g;
graph_create_graph(&g);
mst_prim(&g);
return 0;
}
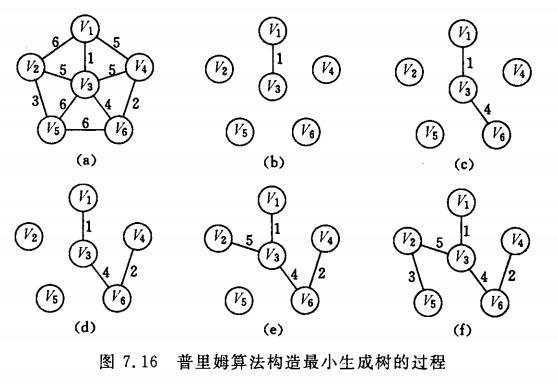
测试图如下:
测试数据:
6 1 2 3 4 5 6 10 1 2 6 1 3 1 1 4 5 2 3 5 2 5 3 3 4 5 3 5 6 3 6 4 4 6 2 5 6 6
上面实线的这个Prim算法的时间复杂读是O(n^2),主要耗费在选取min cost上。而这一过程,可以用堆(优先队列)实现,使得复杂度降低为O((V+E)*logV)。
由此,Prim算法适用于稠密图中求最小生成树。
2、Kruskal(克鲁斯卡尔)算法
Kruskal适用于稀疏图中求最小生成树。
时间复杂度是O(E log E) 或者 O(E log V)
Kruskal算法的流程非常简单明了,但需要借助两个数据结构:
(1) 堆(优先队列),按照每条Arc的weight,每次取出最小的weight的Arc。
(2) 并查集,用于判断两个顶点vex i和vex j是否属于同一个结合,并可做合并操作。
算法流程:
- create a forest F (a set of trees), where each vertex in the graph is a separate tree
- create a set S containing all the edges in the graph
- while S is nonemptyand F is not yet spanning
- remove an edge with minimum weight from S
- if that edge connects two different trees, then add it to the forest, combining two trees into a single tree
- otherwise discard that edge.
由于实在不喜欢STL的优先队列,用Java实现吧。
首先是并查集,一定不要实现错哦!
public class UFSet {
public UFSet(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int Find(int i) {
// check
if (i < 0 || i >= parent.length) {
return -1;
}
// Find until root and remember it
if (parent[i] != i) {
parent[i] = Find(parent[i]);
}
return parent[i];
}
public void Union(int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= parent.length || j >= parent.length) {
return;
} else {
int pi = Find(i);
int pj = Find(j);
parent[pi] = pj;
}
}
private int parent[] = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 10;
UFSet set = new UFSet(n);
set.Union(0, 3);
set.Union(0, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(set.Find(i));
}
}
}
然后是Kruskal算法,input是输入参数,kruskal是算法正常执行。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Kruskal {
class Arc {
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public Arc(int a, int b, int w) {
x = a;
y = b;
weight = w;
}
private int x; // ivex for start
private int y; // ivex for end
private int weight;
};
int vex2i(int vexs[], int v) {
for (int i = 0; i < vexs.length; i++) {
if (v == vexs[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public void input() {
// Scanner
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// Get vexs
int nvexs = 0;
System.out.println("Please enter the number of vexs:");
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
nvexs = scan.nextInt();
}
vexs = new int[nvexs];
for (int i = 0; i < nvexs; i++) {
System.out.println("Please enter a integer for vex[" + i + "]:");
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
vexs[i] = scan.nextInt();
}
}
// PriorityQueue to store arcs
pq = new PriorityQueue<Arc>(100, new Comparator<Arc>() {
@Override
public int compare(Arc a1, Arc a2) {
return a1.getWeight() - a2.getWeight();
}
});
// Get arcs
int narcs = 0;
System.out.println("Please enter the number of arcs:");
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
narcs = scan.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < narcs; i++) {
System.out.println("Please enter x y w for arc[" + i + "]:");
int x = -1, y = -1, w = 0;
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
x = scan.nextInt();
x = vex2i(vexs, x);
}
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
y = scan.nextInt();
y = vex2i(vexs, y);
}
if (scan.hasNextInt()) {
w = scan.nextInt();
}
if (x == -1 || y == -1) {
System.out.println("x or y invalid.");
i--;
continue;
}
if (w <= 0) {
System.out.println("w invalid.");
i--;
continue;
}
Arc arc = new Arc(x, y, w);
pq.add(arc);
}
}
public void kruskal() {
// Union-Find Set
UFSet ufset = new UFSet(vexs.length);
// while not pq.empty, select min arc.w
double ans = 0.0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Arc arc = pq.poll();
int x = arc.getX();
int y = arc.getY();
int px = ufset.Find(x);
int py = ufset.Find(y);
if (px == py) {
continue;
} else {
System.out.println("Arc " + vexs[x] + " ->" + vexs[y] + "");
ufset.Union(x, y);
ans += arc.getWeight();
}
}
System.out.println("Final mst: " + ans);
}
private int vexs[] = null;
private PriorityQueue<Arc> pq = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Kruskal kruskal = new Kruskal();
// Input vexs and arcs
kruskal.input();
// Doing Kruskal
kruskal.kruskal();
}
}
输出结果:
Arc 1 ->3 Arc 4 ->6 Arc 2 ->5 Arc 3 ->6 Arc 2 ->3 Final mst: 15.0